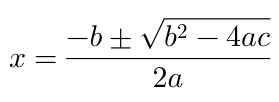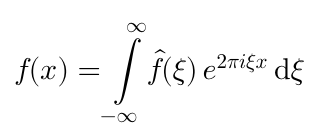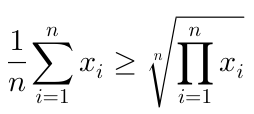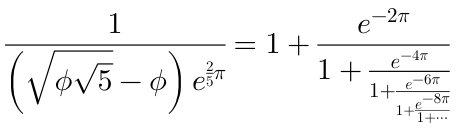iosMath 0.9.4
| TestsTested | ✓ |
| LangLanguage | Obj-CObjective C |
| License | MIT |
| ReleasedLast Release | May 2017 |
Maintained by Kostub Deshmukh.
iosMath 0.9.4
- By
- Kostub Deshmukh
iosMath is a library for displaying beautifully rendered math equations
in iOS and MacOS applications. It typesets formulae written using the LaTeX in
a UILabel equivalent class. It uses the same typesetting rules as LaTeX and
so the equations are rendered exactly as LaTeX would render them.
It is similar to MathJax or
KaTeX for the web but for native iOS or MacOS
applications without having to use a UIWebView and Javascript. More
importantly, it is significantly faster than using a UIWebView.
Examples
Here are screenshots of some formulae that you could render with this library:
The EXAMPLES.md file contains more examples.
Requirements
iosMath works on iOS 6+ or MacOS 10.8+ and requires ARC to build. It depends
on the following Apple frameworks:
- Foundation.framework
- CoreGraphics.framework
- QuartzCore.framework
- CoreText.framework
Additionally for iOS it requires:
- UIKit.framework
Additionally for MacOS it requires:
- AppKit.framework
Installation
Static library
You can also add iosMath as a static library to your project or workspace.
- Download the latest code version or add the repository as a git submodule to your git-tracked project.
- Open your project in Xcode, then drag and drop
iosMath.xcodeprojonto your project or workspace (use the "Product Navigator view"). - Select your target and go to the Build phases tab. In the Link Binary
With Libraries section select the add button. On the sheet find and
add
libIosMath.a. You might also need to addiosMathto the Target Dependencies list. - Add the
MathFontBundleto the list ofCopy Bundle Resources. - Include IosMath wherever you need it with
#import <IosMath/IosMath.h>.
Usage
The library provides a class MTMathUILabel which is a UIView that
supports rendering math equations. To display an equation simply create
an MTMathUILabel as follows:
#import "MTMathUILabel.h"
MTMathULabel* label = [[MTMathUILabel alloc] init];
label.latex = @"x = \\frac{-b \\pm \\sqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}";
Adding MTMathUILabel as a sub-view of your UIView as will render the
quadratic formula example shown above.
Included Features
This is a list of formula types that the library currently supports:
- Simple algebraic equations
- Fractions and continued fractions
- Exponents and subscripts
- Trigonometric formulae
- Square roots and n-th roots
- Calculus symbos - limits, derivatives, integrals
- Big operators (e.g. product, sum)
- Big delimiters (using \left and \right)
- Greek alphabet
- Combinatorics (\binom, \choose etc.)
- Geometry symbols (e.g. angle, congruence etc.)
- Ratios, proportions, percents
- Math spacing
- Overline and underline
- Math accents
- Matrices
- Equation alignment
- Change bold, roman, caligraphic and other font styles (\bf, \text, etc.)
- Most commonly used math symbols
Example
There is a sample app included in this project that shows how to use the
app and the different equations that you can render. To run the sample
app, clone the repository, and run pod install first. Then on iOS run the
iosMathExample app. For MacOS run the MacOSMath app.
Advanced configuration
MTMathUILabel supports some advanced configuration options:
Math mode
You can change the mode of the MTMathUILabel between Display Mode
(equivalent to $$ or \[ in LaTeX) and Text Mode (equivalent to $
or \( in LaTeX). The default style is Display. To switch to Text
simply:
label.labelMode = kMTMathUILabelModeText;Text Alignment
The default alignment of the equations is left. This can be changed to center or right as follows:
label.textAlignment = kMTTextAlignmentCenter;Font size
The default font-size is 20pt. You can change it as follows:
label.fontSize = 30;Font
The default font is Latin Modern Math. This can be changed as:
label.font = [[MTFontManager fontManager] termesFontWithSize:20];This project has 3 fonts bundled with it, but you can use any OTF math font.
Color
The default color of the rendered equation is black. You can change it to any other color as follows:
label.textColor = [UIColor redColor];It is also possible to set different colors for different parts of the
equation. Just access the displayList field and set the textColor
on the underlying displays that you want to change the color of.
Custom Commands
You can define your own commands that are not already predefined. This is similar to macros is LaTeX. To define your own command use:
[MTMathAtomFactory addLatexSymbol:@"lcm"
value:[MTMathAtomFactory operatorWithName:@"lcm" limits:NO]];This creates a \lcm command that can be used in the LaTeX.
Content Insets
The MTMathUILabel has contentInsets for finer control of placement of the
equation in relation to the view.
If you need to set it you can do as follows:
label.contentInsets = UIEdgeInsetsMake(0, 10, 0, 20);Error handling
If the LaTeX text given to MTMathUILabel is
invalid or if it contains commands that aren't currently supported then
an error message will be displayed instead of the label.
This error can be programmatically retrieved as label.error. If you
prefer not to display anything then set:
label.displayErrorInline = NO;Future Enhancements
Note this is not a complete implementation of LaTeX math mode. There are some important pieces that are missing and will be included in future updates. This includes:
- Support for explicit big delimiters (bigl, bigr etc.)
- Addition of missing plain TeX commands
Related Projects
For people looking for things beyond just rendering math, there are two related projects:
- MathEditor: A WYSIWYG editor for math equations on iOS.
- MathSolver: A library for solving math equations.
License
iosMath is available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.
Fonts
This distribution contains the following fonts. These fonts are licensed as follows:
- Latin Modern Math: GUST Font License
- Tex Gyre Termes: GUST Font License
- XITS Math: Open Font License