RSTCoreDataKit 0.1.2
| TestsTested | ✓ |
| LangLanguage | Obj-CObjective C |
| License | BSD 3.0 |
| ReleasedLast Release | Dec 2014 |
Maintained by Jesse Squires, Jesse Squires.
RSTCoreDataKit 0.1.2
- By
- Rosetta Stone
About
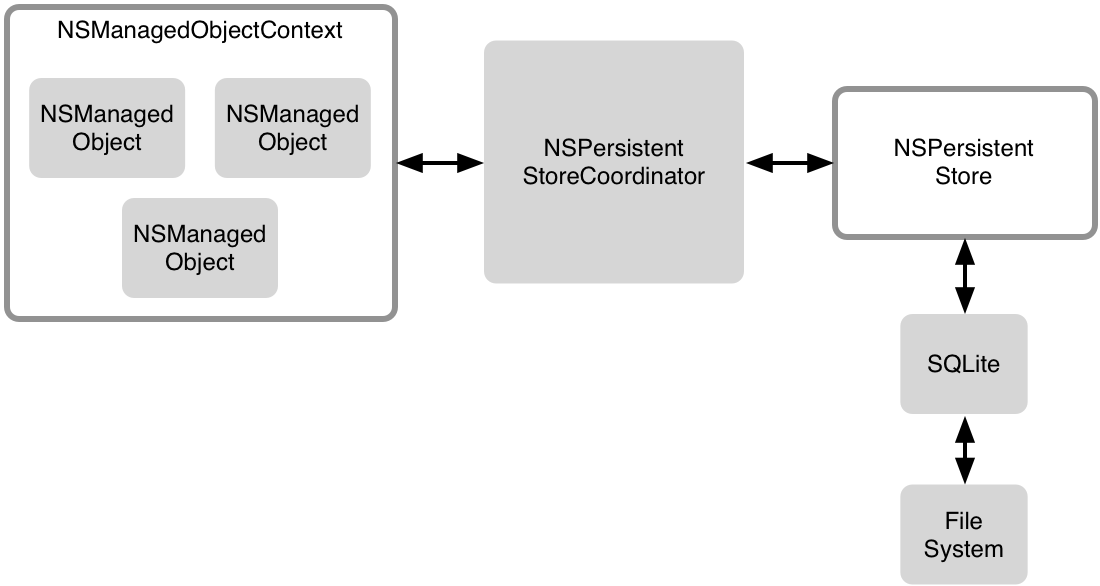
Apple's Core Data framework is notoriously difficult to use, can have a steep learning curve, and involves a lot of boilerplate code just to get started. The goal of this library is to simplify standing up your Core Data stack with a focus on SOLID design principles so that you can quickly get started working with your model. It also provides utilities that make it easier to unit test your model layer.
The Core Data Stack (via objc.io)
Requirements
- iOS 8.0+
- ARC
- Xcode 6+
Installation
# For latest release in cocoapods
pod 'RSTCoreDataKit'
# Feeling adventurous? Get the latest on develop
pod 'RSTCoreDataKit', :git => 'https://github.com/rosettastone/RSTCoreDataKit.git', :branch => 'develop'Getting Started
// New school
@import RSTCoreDataKit;
// Old school
#import <RSTCoreDataKit/RSTCoreDataKit.h>Standing up your Core Data stack
// Initialize the Core Data model, this class encapsulates the notion of a .xcdatamodeld file
// The name passed here should be the name of an .xcdatamodeld file
RSTCoreDataModel *model = [[RSTCoreDataModel alloc] initWithName:@"MyModelName"];
// Initialize the stack
RSTCoreDataStack *stack = [[RSTCoreDataStack alloc] initWithStoreURL:model.storeURL
modelURL:model.modelURL
options:nil
concurrencyType:NSMainQueueConcurrencyType];
// That's all!Alternatively, you can use the convenience initializers for common use cases.
// Same as above, with some default options
RSTCoreDataStack *defaultStack = [RSTCoreDataStack defaultStackWithStoreURL:model.storeURL modelURL:model.modelURL];
// Create a private queue stack
RSTCoreDataStack *privateStack = [RSTCoreDataStack privateStackWithStoreURL:model.storeURL modelURL:model.modelURL];
// Create an in-memory stack
RSTCoreDataStack *inMemoryStack = [RSTCoreDataStack stackWithInMemoryStoreWithModelURL:model.modelURL];Saving a managed object context
NSManagedObjectContext *context = /* an initialized parent or child context */;
BOOL success = [RSTCoreDataContextSaver saveAndWait:context];Deleting your store
RSTCoreDataModel *model = [[RSTCoreDataModel alloc] initWithName:@"MyModelName"];
[model removeExistingModelStore];Checking migrations
RSTCoreDataModel *model = [[RSTCoreDataModel alloc] initWithName:@"MyModelName"];
BOOL needsMigration = [model modelStoreNeedsMigration];Using child contexts
RSTCoreDataStack *stack = /* an initialized stack */;
// Create a child context on a private queue
NSManagedObjectContext *privateChildContext = [stack newDefaultPrivateChildContext];
// Listen for saves from the child context
RSTCoreDataContextDidSaveListener *listener = [[RSTCoreDataContextDidSaveListener alloc] initWithHandler:^(NSNotification *notification) {
// child context was saved
// handle here, merge with parent context, etc.
} forManagedObjectContext:privateChildContext];Unit Testing
RSTCoreDataKit has a suite of unit tests included. You can run them in the usual way from Xcode.
These tests are well commented and serve as further documentation for how to use this library.
Additionally, you should be unit testing your own Core Data model layer. This test suite also serves as an example for how to do this.
// Create an in-memory store for testing purposes
// You can create this before each test, and tear it down after
RSTCoreDataModel *model = [[RSTCoreDataModel alloc] initWithName:@"MyModelName"];
RSTCoreDataStack *inMemoryStackForTesting = [RSTCoreDataStack stackWithInMemoryStoreWithModelURL:model.modelURL];
// Alernatively, you could persist a store to disk for your tests
RSTCoreDataStack *defaultStackForTesting = [RSTCoreDataStack defaultStackWithStoreURL:model.storeURL modelURL:model.modelURL];
// Then remove the store as needed
[model removeExistingModelStore];Documentation
Sweet documentation is available here via @CocoaDocs.
Other useful resources:
- Apple's Core Data Programming Guide
- objc.io's Issue #4: Core Data
- Ray Wenderlich's Core Data Tutorial for iOS: Getting Started
- Other Core Data Libraries & Utilities
Contributing
See CONTRIBUTING.md.
License
RSTCoreDataKit is released under the BSD 3.0 License. See LICENSE for details.
Copyright © 2014 Rosetta Stone.