ListKit 2.0.0
| TestsTested | ✗ |
| LangLanguage | SwiftSwift |
| License | MIT |
| ReleasedLast Release | Jan 2017 |
| SwiftSwift Version | 3.0 |
| SPMSupports SPM | ✗ |
Maintained by Benjamin Encz.
ListKit 2.0.0
- By
- Benjamin Encz
- benjaminencz
Looking for Swift 3 support? Look no further.
ListKit
ListKit allows you to use table views in your app without implementing the UITableViewDataSource protocol yourself. The framework provides different ways to initialize a table view with custom cells. ListKit uses generics to ensure that the content displayed in the table view matches the custom cells you are providing.
Instead configure a data source with your content and your custom cell:
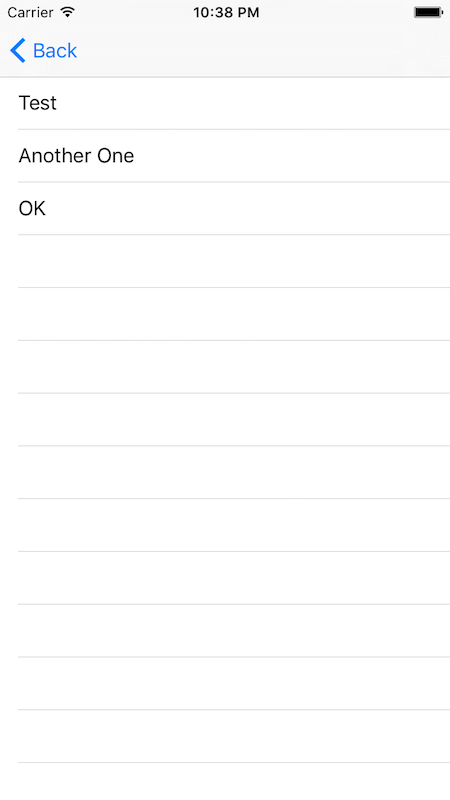
dataSource = ArrayDataSource(array: ["Test", "Another One", "OK"], cellType: CustomTableViewCell.self)
tableView.dataSource = dataSource
Installation
Usage
You can find both examples below as part of the demo project in this repository.
Table View with Simple Custom Cell
A table view that doesn’t require a cell with a XIB file can be implemented as following:
class CustomTableViewCell: UITableViewCell, ListKitCellProtocol {
var model: String? {
didSet {
self.textLabel!.text = model as String?
}
}
}
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var tableView: UITableView!
var dataSource: ArrayDataSource<CustomTableViewCell, String>?
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
dataSource = ArrayDataSource(array: ["Test", "Another One", "OK"], cellType: CustomTableViewCell.self)
tableView.dataSource = dataSource
}
}The most relevant steps for this setup are:
- The
CustomTableViewCellneeds to implement theListKitCellProtocol. That requires defining amodelproperty with the type of content the cell can store. - The
ArrayDataSourceneeds to be configured with the types of the both the custom cell and the type of content stored in the cell. - The
ArrayDataSourceneeds to be initialized with the custom cell type and optionally with the initial content of the table view, represented by an array.
The result will look like this:
Table View with Custom Cell in XIB File
If you want to use a custom cell that’s layout is defined by a XIB file you need to use a slightly different API.
You will likely create a separate Swift file for your custom cell, it needs to implement the ListKitCellProtocol:
class CityCell: UITableViewCell, ListKitCellProtocol {
@IBOutlet var mainImageView: UIImageView!
@IBOutlet var subLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet var mainLabel: UILabel!
var model: City? {
didSet {
if mainLabel != nil {
configureCell()
}
}
}
override func awakeFromNib() {
super.awakeFromNib()
configureCell()
}
func configureCell() {
mainLabel.text = model?.name
subLabel.text = model?.country
mainImageView.image = model?.image
}
}From within your view controller you can configure the table view and data source as following:
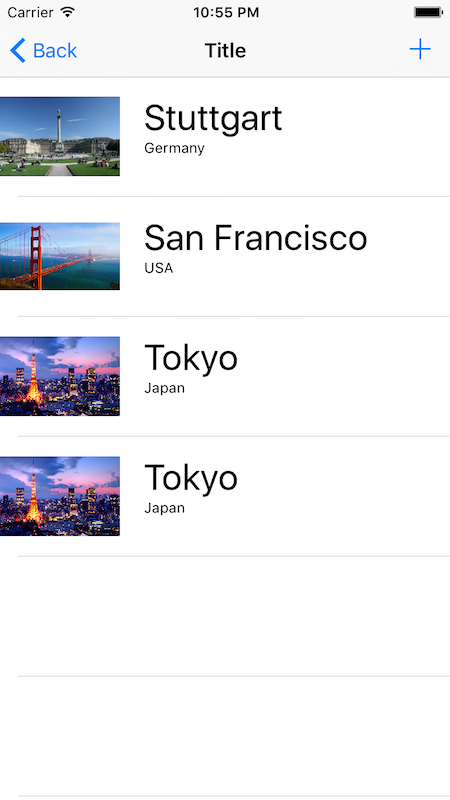
let cities = [city1, city2]
let nib = UINib(nibName: "CityCell", bundle: NSBundle.mainBundle())
dataSource = ArrayDataSource(array: cities, cellType: CityCell.self, nib: nib)
tableView.dataSource = dataSourceThe setup is very similar to the first example, however you now need to provide a nib name additionally to the type of the custom cell.
The result from the demo looks as following:
Acknowledgements
I first encountered the idea of an ArrayDataSource in objc.io issue #1. This microframework is based on the idea from the article. This project takes a slightly different approach and also adds type safety by leveraging Swift generics.